Ensuring Files to SQL Server
Until now, we only had the option to stream files to a SharePoint environment by making use of the Ensure File building block. Lately we received more and more requests to make it possible to also stream files to an Sql server so we added this feature.
Prerequisites
To be able to use filestreaming on an Sql server, a few settings need to be in place. If you want to know more about filestreams on an Sql server, please read the Sql server filestream documentation.
Enable Filestream in the Configuration Manager
- Open up the Sql Server Configuration Manager
Open up the properties of your Sql Server instance
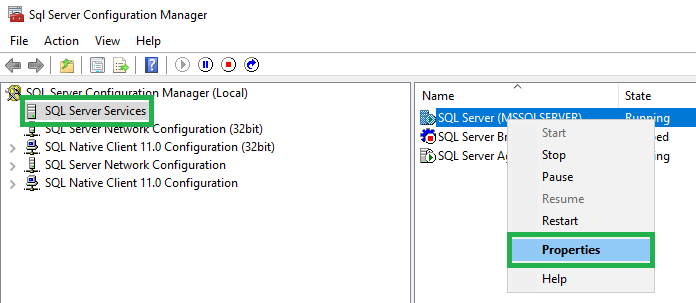
Click on the FILESTREAM tab and check the Enable FILESTREAM for Transact-SQL access box
Check the Enable FILESTREAM for file I/O access
Click OK
- Restart the Sql Server instance via Sql Management Studio or via Windows Services
Warning
If you don't restart the Sql Server instance, you will not be able to use filestreams.
Create Filestream Filegroup
Next we need to create a filestream filegroup on the database which we want to use for files.
Open up Sql Management Studio and navigate to the properties of your database
Click on Filegroups
Click on Add Filegroup and give the new filegroup a meaningful name (in this example: Files)

Create Filestream Data File
After creating the filegroup, we need to create the actual database file in this new filegroup.
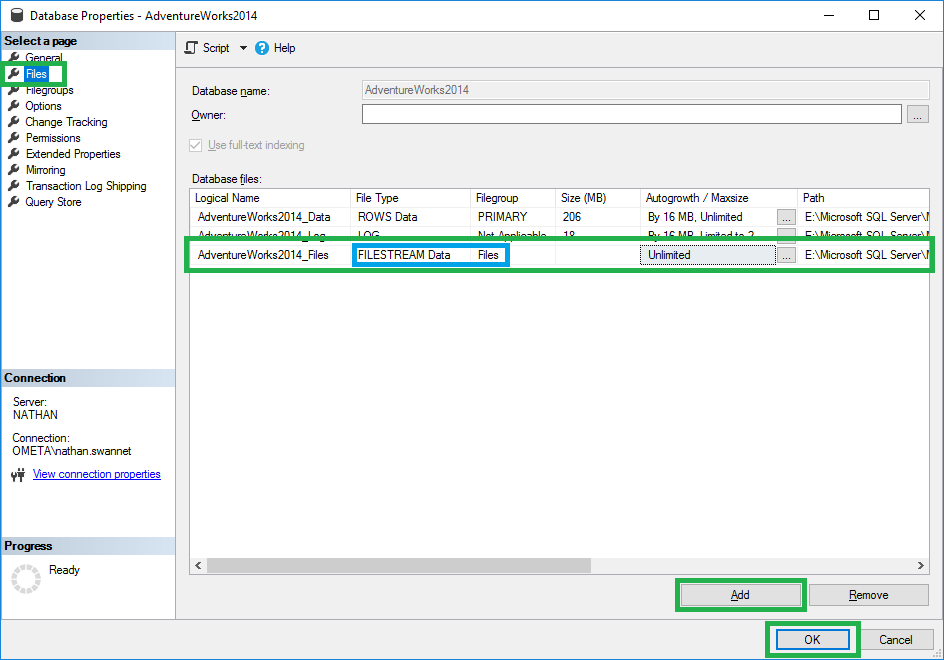
- Still on the properties of your database, navigate to Files
- Click on Add
- Choose the File Type FILESTREAM Data
- Choose your newly created Filegroup
Give the new file a logical name and click OK to exit the properties
Sql Table Configuration
To be able to actually stream files to a table, you'll need to create a filestream column on a table of your choice. This is an example of how you can create a table with a filestream column on the default filestream filegroup:
USE [AdventureWorks2014]
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Files] (
[Id] [uniqueidentifier] ROWGUIDCOL NOT NULL,
[Filename] [nvarchar](100) NULL,
[Filecontents] [varbinary](max) FILESTREAM NULL,
UNIQUE NONCLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
))
GO
Warning
You need a UNIQUE column of the type uniqueidentifier which represents the ROWGUIDCOL. In the above snippet, this is the Id column. Sql will throw an error if this column does not exist.
Streaming Files with Ometa
Now that you're ready to stream files to your Sql server, let's dive into the required configuration in Ometa.
Profile
First, you'll need a profile based on the new Sql Utilities template. Create a profile and fill in the required fields.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Sql Connection String | The connection string to your sql server. For more information see this article |
Note
We strongly suggest to use Integrated Security=true; in your connection string. This way, the user of the BCSL service will be used to authenticate against the Sql server.
Method
By default, there is already a method in the Ometa.Utilities object named Ensure Sql File which can be used for streaming a file to a table of your choice. However, since you likely want to set some extra fields on your sql record, you can create your own method with the necessary input fields.
When creating your own method, you'll need to configure the interface script like this:
Ometa.Utilities.Client.dll
SqlFilestreamUtilities
Table Name=
Filestream Column Name=
Where Clause=
The first 2 lines of the interface script defines the class which will be used by your method. These are fixed. The other lines are explained below.
Set this to the name of the sql table you want to stream files to. You can set this to a fixed value or use context values in the format Table Name={$Context Name}.
It is allowed to include the database and schema name. E.g.: Table Name=AdventureWorks2014.dbo.Files.
Important
An error will be thrown if the table name is not filled in or cannot be found.
When executing the method, all input/context fields which match with columns in your sql table will be used to set/update their values.
A match is made by:
- comparing the name of the input/context field with the name of the sql column
- comparing the external name of the input field with the name of the sql column
Warning
When an input/context field can be matched with the special ROWGUID column and that field contains a valid GUID value, that GUID value will be used to find the record which must be updated.
If no record can be found based on that GUID value, an error will be thrown. A new record will not be created in this case.
If you create an output field which matches the ROWGUID column, records will be returned with the ROWGUID's which have been created.