⚠️ Security Advisory: SharePoint Online CSP Enforcement
| Status | Announced |
| Enforcement Date | March 1, 2026 (or June 1, 2026, if postponed) |
| Impact | High (Potential breaking change for SPFx components) |
| Microsoft Reference | CSP Trusted Script Sources |
Summary
Microsoft is improving SharePoint Online security by enforcing Content Security Policy (CSP). Currently, CSP is applied in "reporting mode", but starting March 1, 2026, this policy will be strictly enforced.
What does this mean?
- External Scripts: JavaScript files loaded from servers not explicitly marked as "Trusted" in SharePoint will be blocked.
- Inline Scripts: Code directly embedded in HTML (e.g.,
<script>...</script>oronclick="...") will be blocked.
How this affects your solution
1. Ometa Core Dependencies (Configuration Required):
The ADM and other Ometa Web Parts load external scripts hosted on the Ometa Core Service / IIS Server. To ensure continued operation, the Core Service URL must be explicitly added to the SharePoint "Allow List." This requires manual configuration (see Action Plan).
2. Custom Renderers & Conversion Scripts:
When creating Custom Renderers or Conversion Scripts, you use Inline Scripts to register click functions. SharePoint's CSP will block these. To resolve this, Ometa will create event listeners based on the Inline Scripts for you. This means that no changes are needed in the configuration.
Many solutions use Custom Renderers or Conversion Scripts containing inline scripts. Under strict CSP, patterns like the ones below would normally break:
Example of Custom Renderer
Ometa will take the inline onclick function and create a click event listener that executes the script.
const templateFunction = function(rowData, formattedData, csl) {
let productName = rowData.productName;
return `
<!-- The onclick is an inline event which will be converted. -->
<div class="card" onclick="window.myNamespace.processAction()">
${productName}
</div>
`;
}
Conversion Scripts
A common practice is to use a conversion script to create HTML tags to will be shown in the Multi Record.
- Inline event handlers:
Ometa will take the inline onclick function and create a click event listener that executes the script someFunction.
```C#
Value = "<div onclick='someFunction()'>Click Me</div>"
```
- Javascript protocols in links:
Ometa will take the inline JavaScript function from the href and create a click event listener that executes the script someFunction.
```C#
Value = "<a href='javascript:someFunction()'>Click Me</a>"
```
Other CSP Violation examples
Any
<script>block which goes directly to HTML:<script>console.log('Hello');</script>Inline Event Handlers (JavaScript embedded in HTML attributes):
<button onclick="alert('Hi')">Click</button> <body onload="init()">...</body>const testDiv = document.createElement('div'); testDiv.setAttribute('onclick', "alert('Hi')"); testDiv.click();JavaScript embedded in
hreforsrcattributes:<a href="javascript:alert('Hi')">Click</a>Dynamically Created Inline Scripts:
const s = document.createElement('script'); s.textContent = "alert('Hi')"; document.head.appendChild(s);InnerHTMLorinsertAdjacentHTMLwith<script>:element.innerHTML = "<script>alert('Hi')</script>";
Our Solution: Backward Compatibility Hotfix
You likely do not need to rewrite your code.
Ometa is currently working on a hotfix aimed at resolving these inline script issues automatically. This update is designed to make existing Custom Renderers and Conversion Scripts compatible with the new CSP rules without requiring you to manually refactor your code.
Note
Strategic Advice: Use Cards
While our hotfix aims to keep Custom Renderers working, we strongly advise using the Cards module for all new configurations. The Cards module is the preferred, future-proof alternative to Custom Renderers.
Custom Added HTML Elements
When custom HTML elements are manually added to the ADM, Ometa cannot automatically detect or convert them. These elements may include inline events, which will be blocked by CSP.
To fix this, the inline events need to be converted to event listeners. Ometa has a helper function that will do this for you makeElementsCspCompliant(myElement).
makeElementsCspCompliant
This helper function scans an HTML element for inline event handlers (e.g., onclick, onload) and automatically converts them to CSP-compliant event listeners.
Patcher
The patcher automatically applies makeElementsCspCompliant to all elements in scripts using innerHTML.
Examples
Action Plan
Step 1: Add Trusted Sources (MANDATORY)
Regardless of the hotfix, you must explicitly trust your Ometa Core Service URL. The software cannot do this for you.
- Go to the SharePoint Online Admin Center.
- Navigate to Advanced > Script sources.
- Add the URL of your Ometa Core Service (e.g.,
https://ometa.coreservice.com).

Step 2: Postpone Enforcement (Highly Recommended)
We aim to release the hotfix before the March 1st deadline. However, to ensure business continuity and allow sufficient time for testing and deployment, we strongly advise all customers to apply for the postponement.
This extends the deadline to June 1, 2026, creating a safe buffer for your upgrade.
Important
Only run this command after February 9, 2026. If you do this before, the setting is not persisted.
Run the following PowerShell command after February 9, 2026. (available in SPO Management Shell version 16.0.26712.12000 or higher):
Set-SPOTenant -DelayContentSecurityPolicyEnforcement $true
Step 3: Audit your environment (Recommended)
Even though we are providing a fix, we recommend auditing your environment to ensure you haven't missed any other external script sources apart from Ometa (e.g., Google Analytics, external widgets) that also need to be added to the Trusted Sources list in Step 1.
Via Browser: Open your SharePoint site, press
F12(DevTools), and check the Console. Look for "Violates Content Security Policy" errors (refer to the next two screenshots).

Via Microsoft Purview: Navigate to the Audit log and search for
ViolatedContentSecurityPolicy.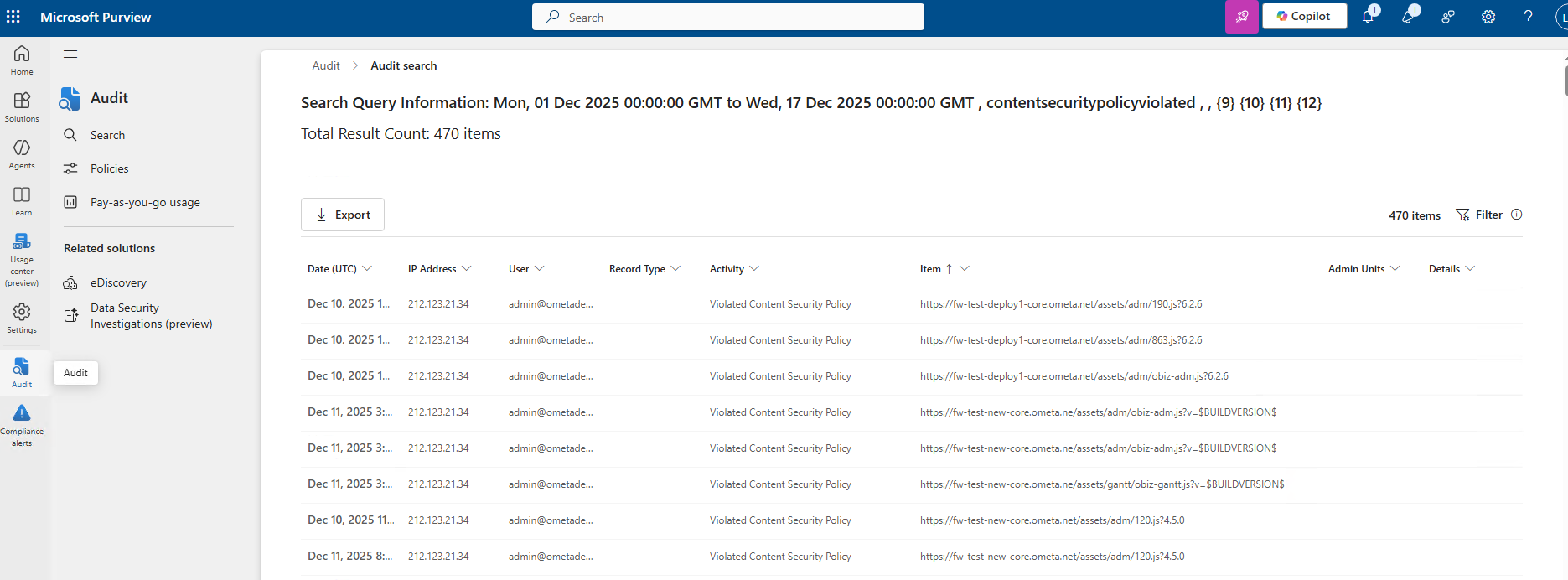
Step 4: Plan your Upgrade
- Wait for the Hotfix: Plan to install the upcoming Ometa framework update or the hotfix for version 6.2.x before March 2026. This will patch the inline script vulnerabilities in Custom Renderers and Conversion Scripts.
- Migrate to Cards (Optional but Recommended): If you are planning major maintenance on a solution, consider replacing Custom Renderers with Cards to reduce technical debt.
Step 5: Upgrade the SharePoint Package
- Upgrade the
obiz-suite-app.sppkgSharePoint Package. This is needed for caching purposes. Refer to the upgrade procedure.
Warning
Ensure the ADM hotfix is applied to all environments prior to upgrading the SharePoint Package. Upgrading the package forces a browser cache invalidation, guaranteeing that users immediately receive the updated, CSP-compliant files.
Step 6: Run the Patcher
Warning
Do not run the patcher, before the SharePoint Package is updated, because of caching purposes.
We have provided an update to the patcher that can either identify the issues or patch them when given the right flags. These flags will make sure the patcher only runs the needed functions for the CSP checks and nothing else.
| Flag | Explanation |
|---|---|
/checkcspissues |
Mandatory. Instructs the patcher to focus exclusively on CSP-related issues. |
/reportonly |
Optional. Scans and reports issues without applying any changes. |
Note
The patcher automatically creates a backup of all objects and scripts before applying any modifications.
Recommended Workflow:
To ensure a controlled update, we recommend following these two steps from the Command Prompt or PowerShell.
The default location for the patcher is %OMETA_INSTALL_ROOT%\Ometa Software Suite\TopDir\BC\Bin.
- Identification Mode (Safe): Run this command first to generate a report of all CSP issues found in your environment without changing anything.
cd C:\Program Files (x86)\Ometa BVBA\Ometa Software Suite\TopDir\BC\Bin\
BCRPatcher.exe /checkcspissues /reportonly

- Patching Mode: After reviewing the report, run the command without the
/reportonlyflag to apply the actual patches.
cd C:\Program Files (x86)\Ometa BVBA\Ometa Software Suite\TopDir\BC\Bin\
BCRPatcher.exe /checkcspissues
Timeline & Postponement
- Now: Reporting mode is active.
- Action: Add Trusted Sources & Identify external dependencies.
- Action: Run the
Set-SPOTenantpostponement script to secure the June deadline.
- Q1 2026: Release of the Ometa CSP Hotfix.
- Action: Update Ometa Framework or apply the hotfix.
- March 1, 2026: Official Microsoft enforcement begins (Safe if postponed).
- June 1, 2026: Final enforcement for delayed tenants. You must have upgraded to the Ometa hotfix or migrated your customizations by this date.